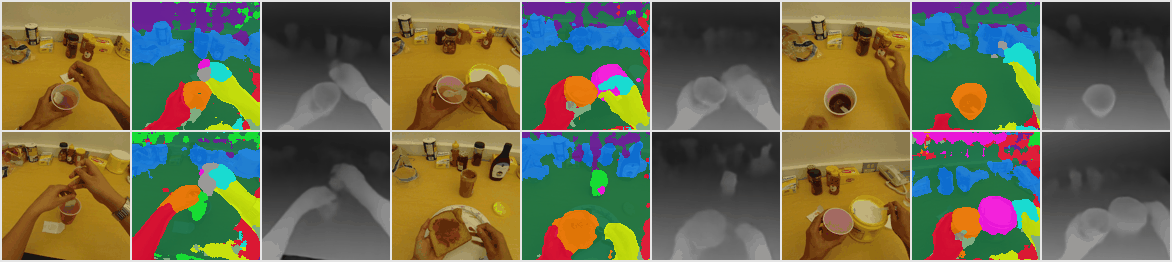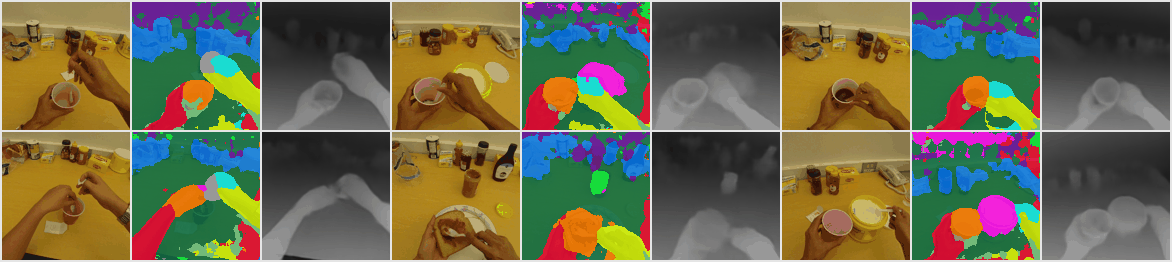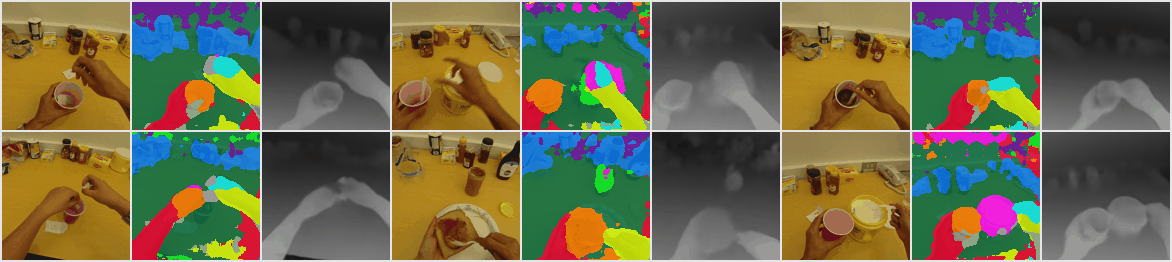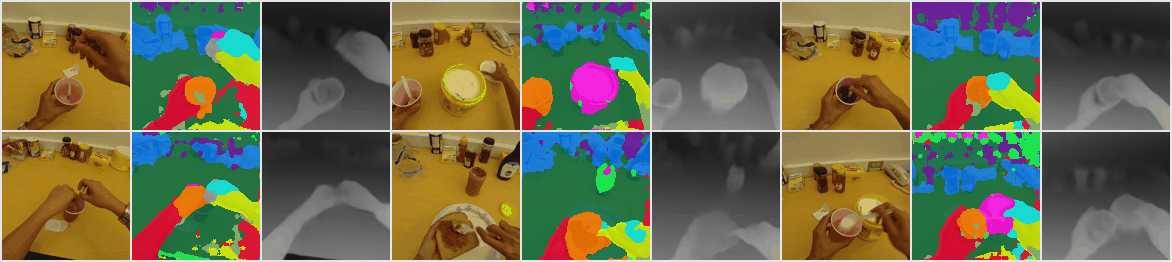
Recent State Space Models (SSMs) such as S4, S5, and Mamba have shown remarkable computational benefits in long-range temporal
dependency modeling. However, many sequence modeling problems, the underlying process is inherently modular and it is of
interest to have inductive biases that mimic this modular structure. In this paper, we introduce SlotSSMs, a novel framework
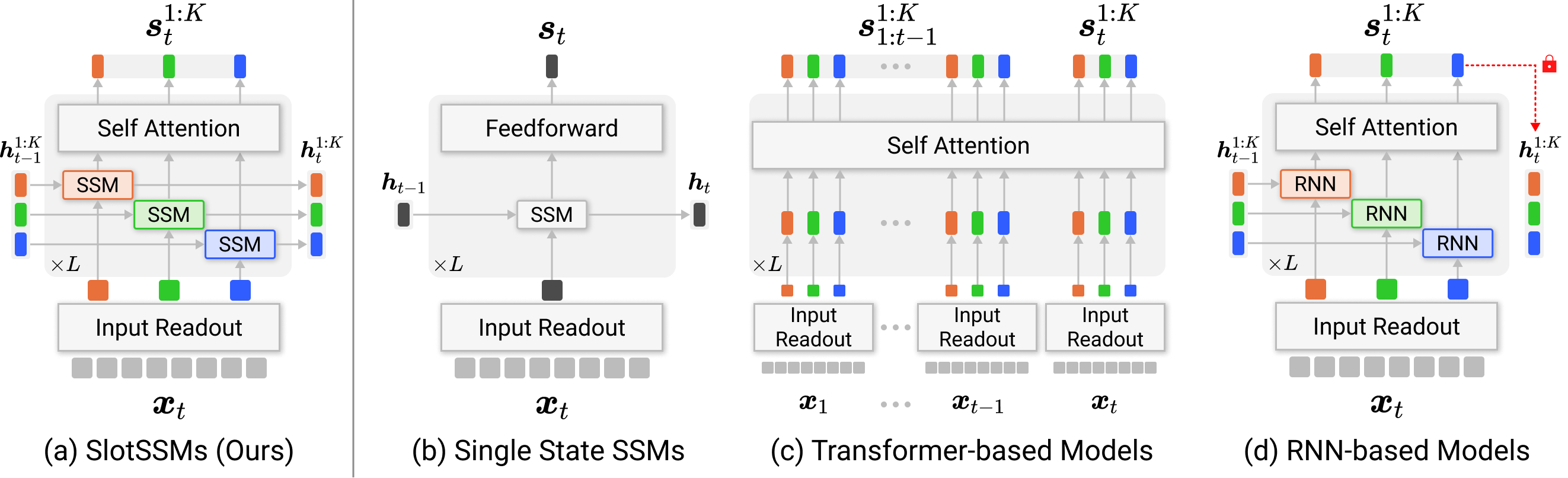
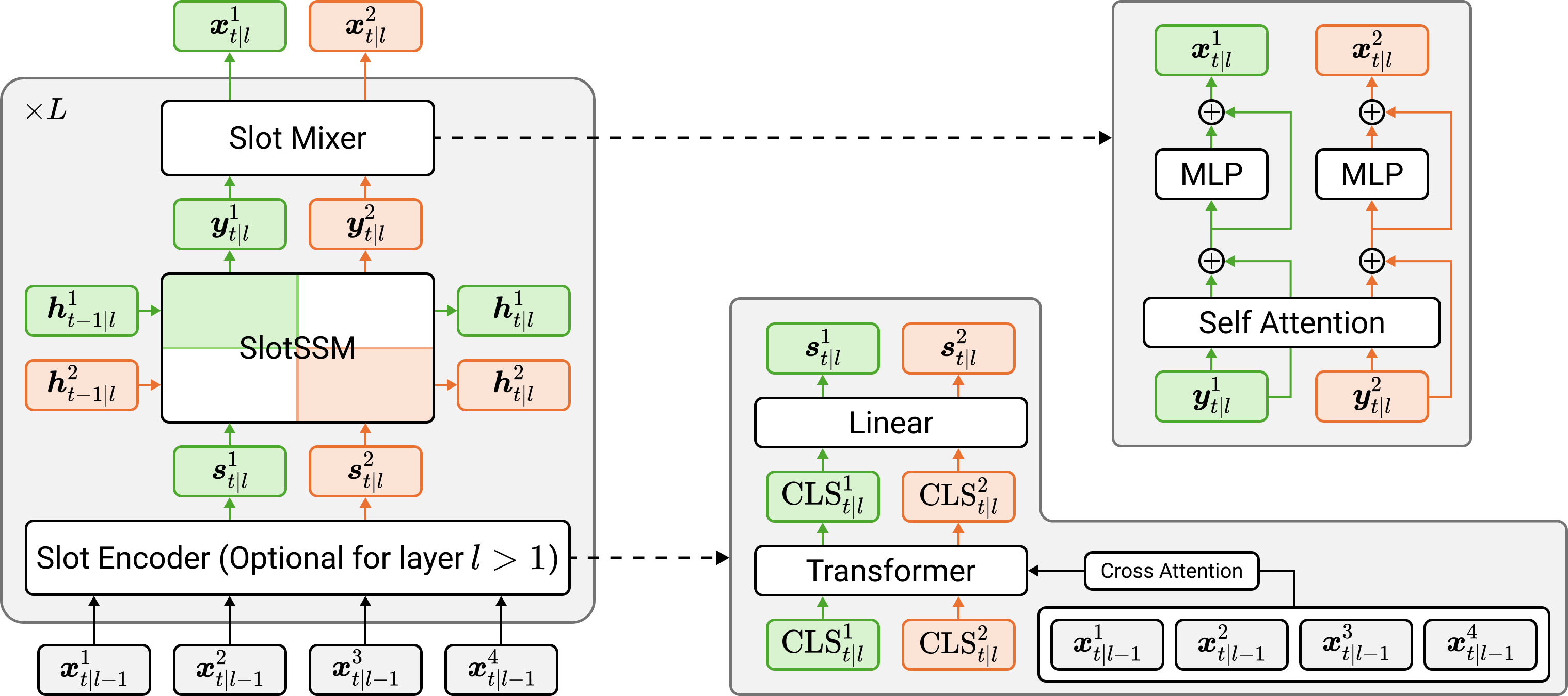
for incorporating independent mechanisms into SSMs to preserve or encourage separation of information. Unlike conventional SSMs
that maintain a monolithic state vector, SlotSSMs maintains the state as a collection of multiple vectors called slots.
Crucially, the state transitions are performed independently per slot with sparse interactions across slots implemented via the
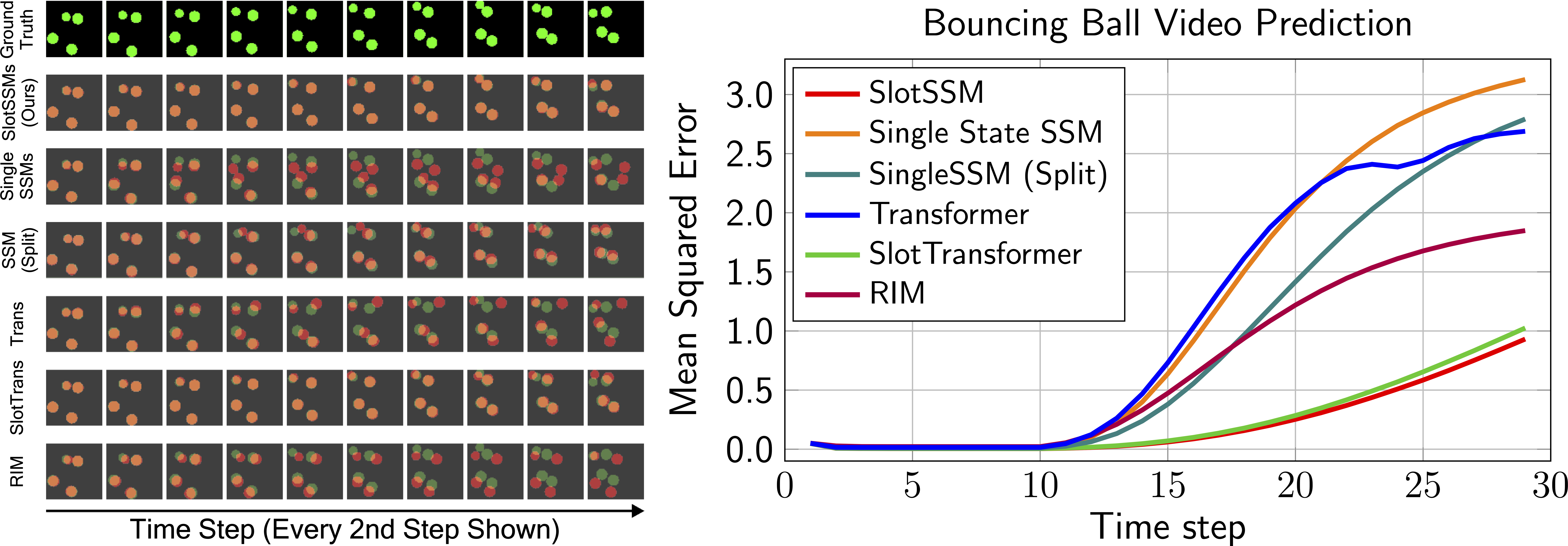
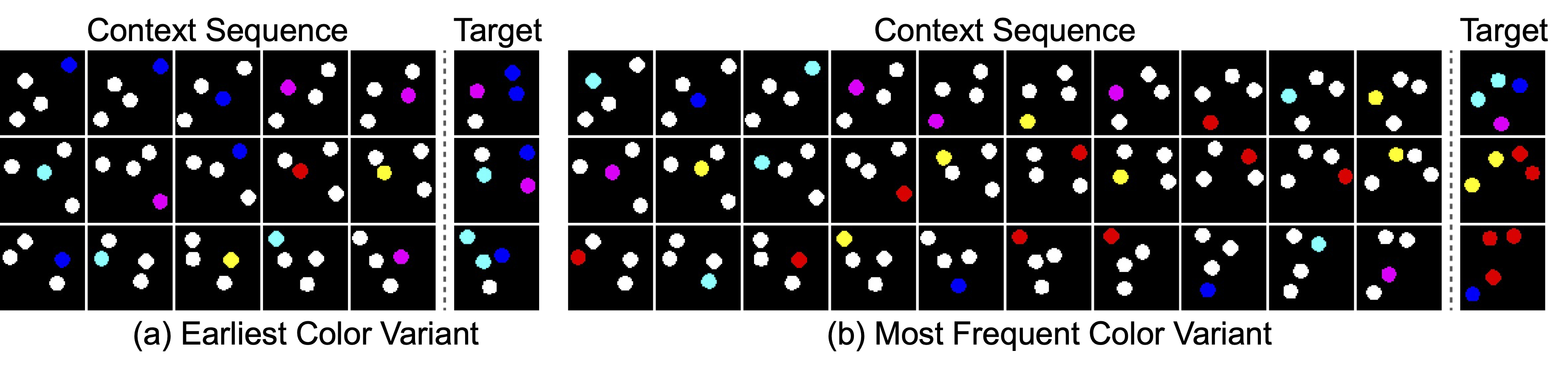
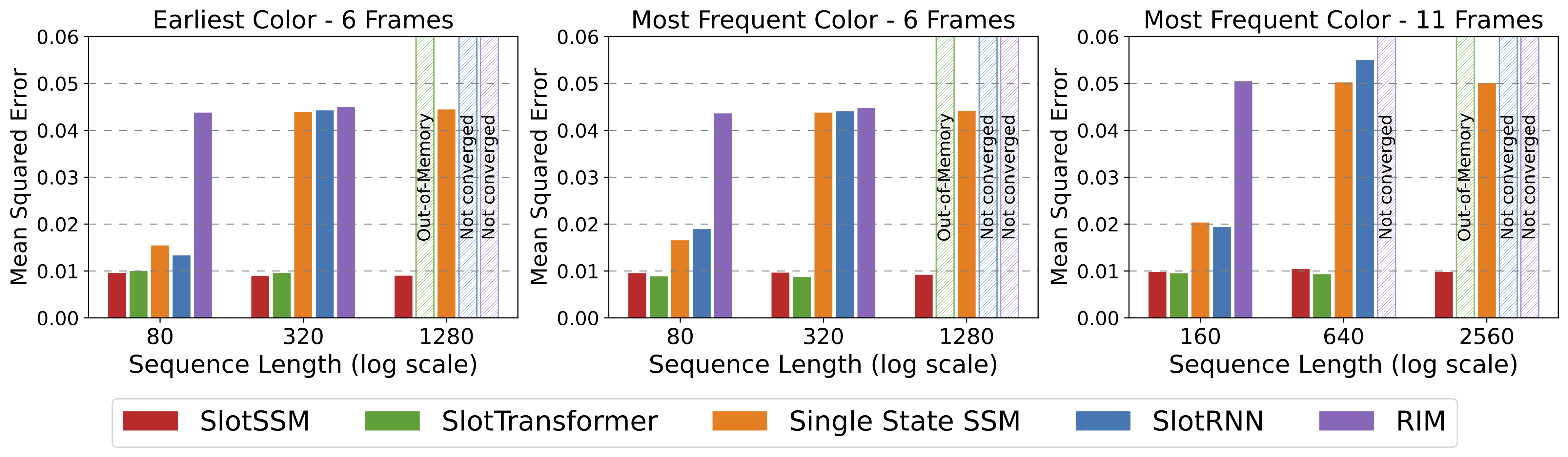
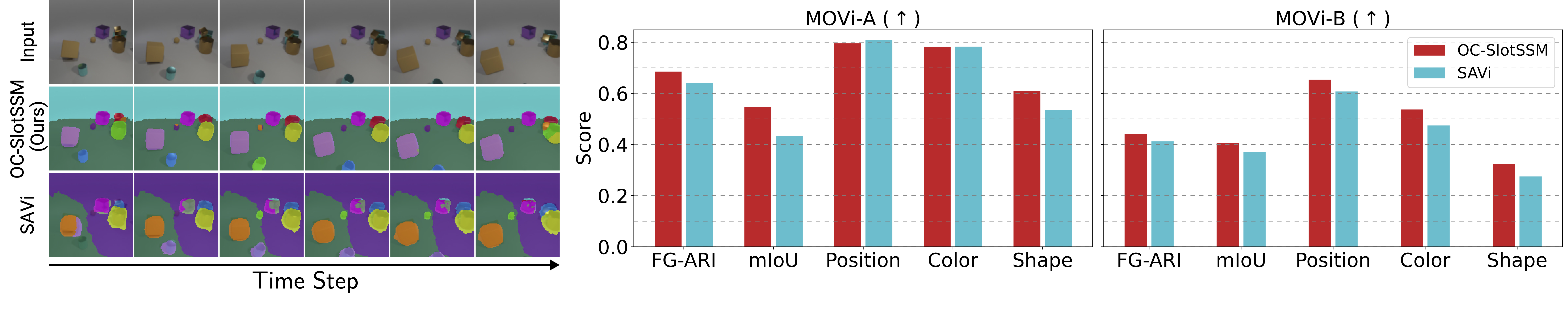
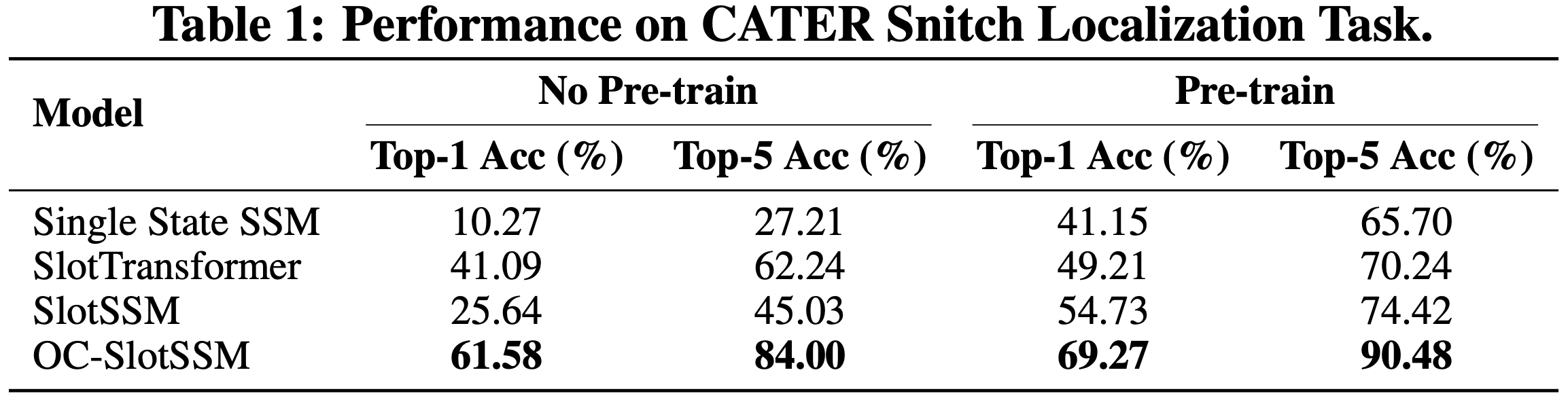
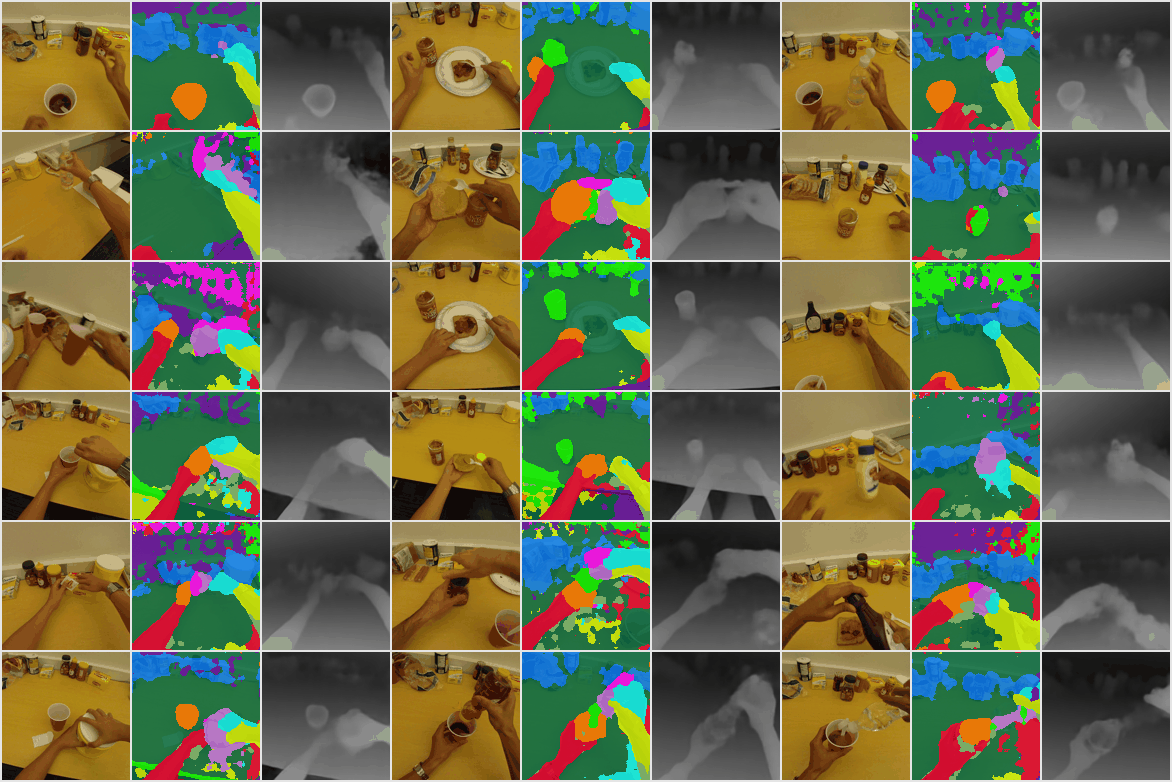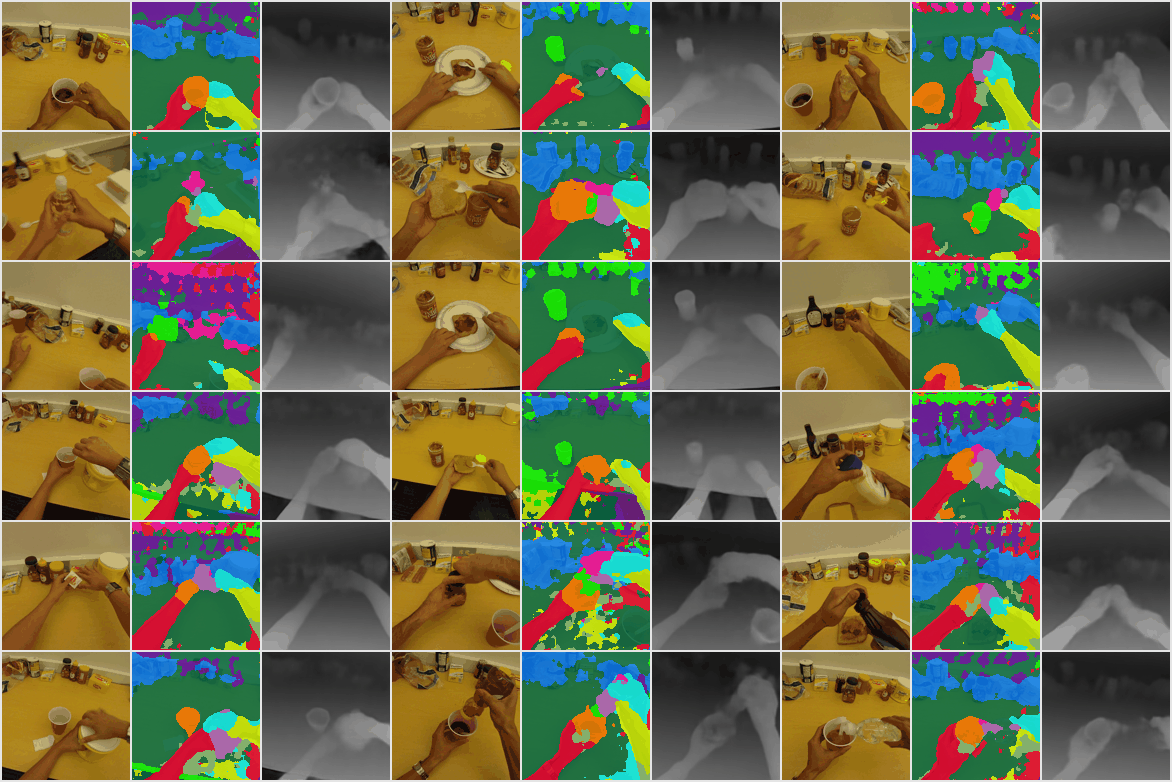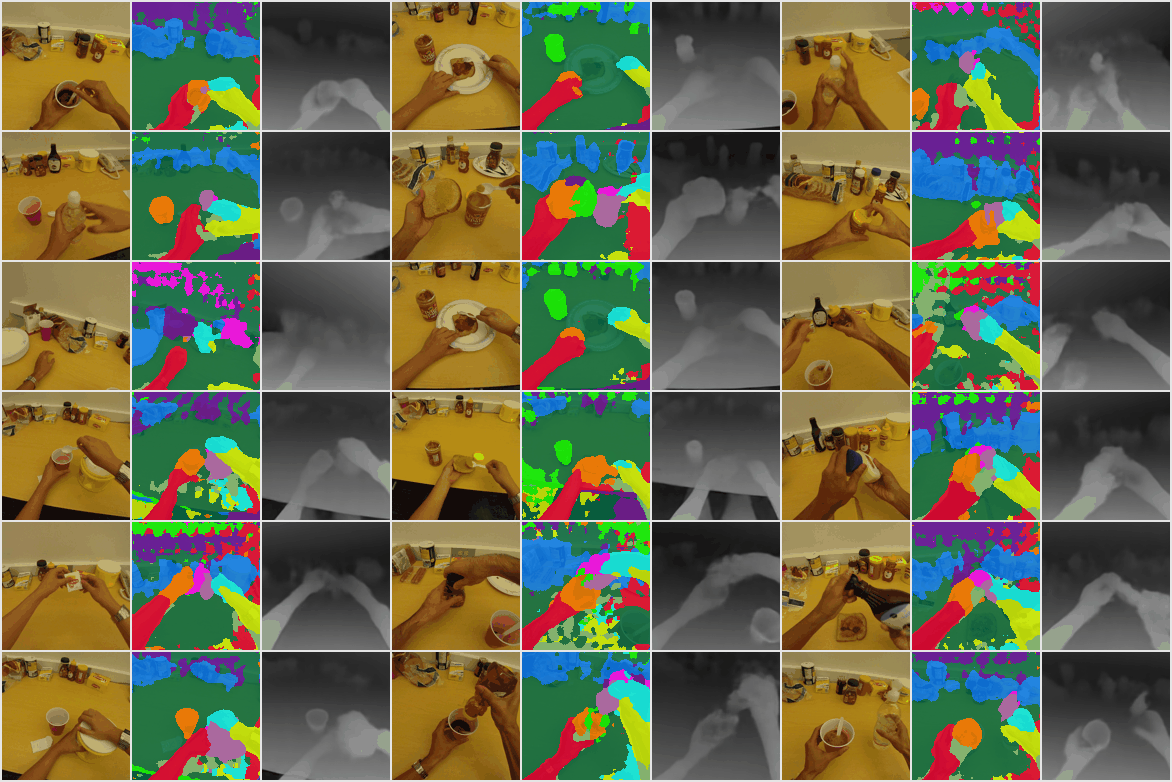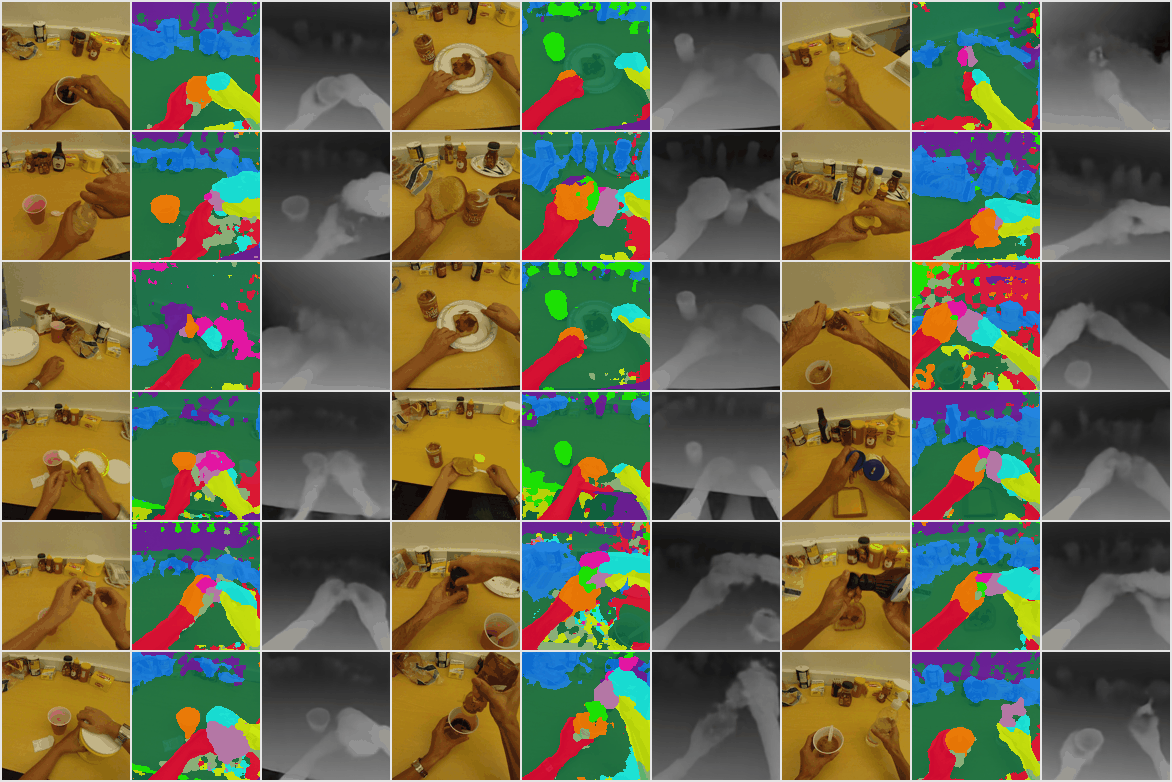
bottleneck of self-attention. In experiments, we evaluate our model in object-centric learning, 3D visual reasoning, and
long-context video understanding tasks, which involve modeling multiple objects and their long-range temporal dependencies.
We find that our proposed design offers substantial performance gains over existing sequence modeling methods.